Map 中的常用方法
增
put(Object key, Object value):添加键值对。putAll(Map m):将指定Map中的所有键值对添加到当前Map中。
删
Object remove(Object key):根据键移除对应的键值对。
改
put(Object key, Object value):更新指定键的值。putAll(Map m):将指定Map中的所有键值对添加到当前Map中。
查
Object get(Object key):根据键获取对应的值。
长度
size():返回Map中键值对的数量。
遍历
- 遍历键集:
Set keySet()。 - 遍历值集:
Collection values()。 - 遍历键值对集:
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet()。
TreeMap的使用
- 底层使用红黑树存储:TreeMap是基于红黑树实现的。
- 排序:可以按照添加的键值对中的键元素的指定属性的大小顺序进行遍历。需要考虑使用自然排序或定制排序。
- 要求:向TreeMap中添加的键必须是同一个类型的对象。
Hashtable与Properties的使用
- Properties:是Hashtable的子类,其键和值都是String类型的,常用来处理属性文件。
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class CityMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//一 获取map 中所有的key
Map map = CityMap.model;
Set provinces = map.keySet();
for (Object province : provinces) {
System.out.println(province + "\t\t");
}
//二 根据提示 西欧你键盘获取省市值,判断省市是否存在,如果存在遍历value中的各个城市,如果不存在,提示用户重新输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] cities;
while (true) {
System.out.print("Enter City Name: ");
String province = sc.next();
//String[]
cities = (String[]) map.get(province);
//获取省份对应各个城市的String[]
if (cities == null) {
System.out.println("No City Found");
}else{
break;
//跳出循环
}
sc.close();
}
for (int i = 0; i < cities.length; i++) {
System.out.println(cities[i]);
}
//三 根据提示 从键盘获取城市,遍历各个城市构成的String[],判断输入的城市是否在此数组中,如果存在,信息登记完毕,如果不存在,提示用户重新输入
}
}
class CityMap {
public static Map model = new HashMap();
static {
model.put("北京",new String[]{"北京"});
model.put("辽宁",new String[]{"沈阳","盘锦"});
}
}
import java.util.*;
//集合 Music List
public class SingerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap singers = new HashMap();
String singer1 = "周杰伦";
ArrayList songs1 = new ArrayList();
songs1.add("夜曲");
songs1.add("晴天");
singers.put(singer1, songs1);
String singer2 = "林俊杰";
ArrayList songs2 = new ArrayList();
songs2.add("江南");
songs2.add("曹操");
singers.put(singer2, songs2);
Set entrySet = singers.entrySet();
Iterator iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iterator.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
}
// out put
//林俊杰 : [江南, 曹操]
//周杰伦 : [夜曲, 晴天]
}
}
自定义泛型类
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GenericTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
//Person<String> person2 = new Person();
//未声明泛型不能使用
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//这个可以使用是它本来就有
}
}
//自定义泛型接口
class A<T>{
}
interface B<T1,T2>{
//可以使用多个参数
}
public class Order<T> {
//声明了类的泛型以后,就可以在类的内部使用此泛型参数
T t;
int orderID;
public Order(int orderID, T t) {
this.orderID = orderID;
this.t = t;
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化是,就可以指明类的泛型参数的类型
Order order = new Order();
Object obj = order.getT;
//泛型参数在指明时,时不可以使用基本数据类型的,但是可以使用包装类替代基本数据类型
Order<int> order1 = new Order<>();
Order<Integer> order2 = new Order<>();
}
}
使用说明
- 我们在声明完自定义泛型以后,可以在内部类,比如(属性,方法,构造器中)使用类的泛型
- 我们在创建自定义泛型的的对象时,可以指明泛型参数类型。一旦指明,内部类凡是使用类的泛型参数的位置,都具体化为指定的类的泛型类型。
- 如果在创建自定义泛型对象时,没有指明泛型参数类型,那么泛型将被擦除,泛型对应的类型均按照 Object 处理,但不等价于 Object。
经验 泛型要是用就全用 不用就全不用
- 泛型的指定中心必须使用引用数据类型。不能使用基本数据类型。此时只能使用包装类替换
- 除创建泛型类的对象外,子类继承泛型时,子类也不确定泛型的类型,则可以继续使用泛型参数。
如果我们在给泛型提供子类时,子类也不确定泛型的类型,则可以继续使用泛型结构中的泛型参数。
我们还可以在现有的父类的泛型基础上,新增泛型。
注意点
- 泛型类可能有多个参数,此时应将多个参数一起放在 尖 括号内 <E1,E2,E3>
- JDK7.0 开始,泛型的简化操作 ArrayList flist = new ArrayList<>();
- 如果泛型结构是一个接口或抽象类,则不可创建泛型的对象。
- 不能使用 new E[]。但可以,E[] elements = (E[]new Object(camacity));
- 参考 ArrayList 源码中声明,Object[] elementData,而非泛型参数类型数组
- 在类/接口 上声明的泛型,在本类或本接口中即代表某种类型,但不可以在静态方法中使用泛型的类型。
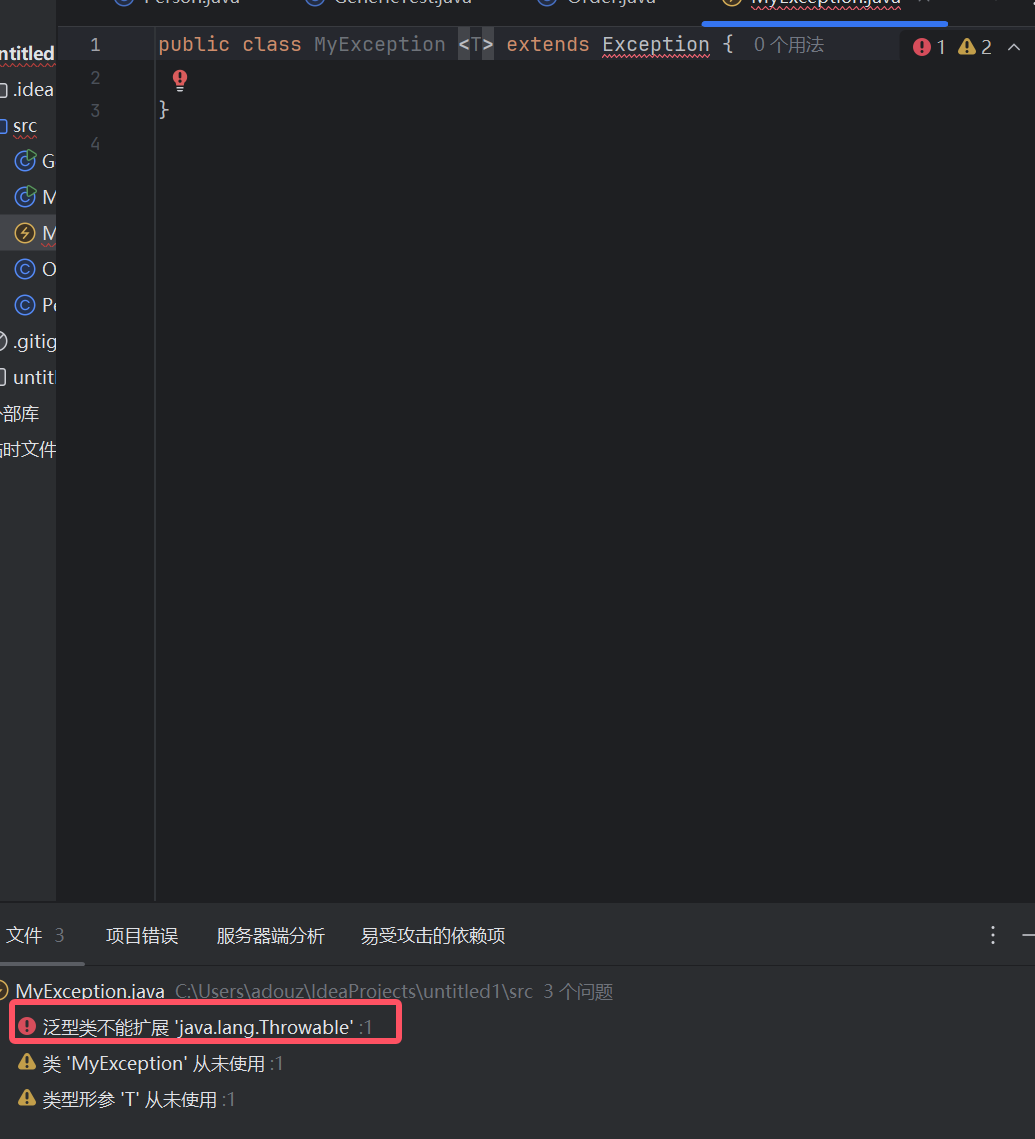
- 异常类时不能带泛型的。
说明
- 声明泛型方法时,一定要添加泛型参数
- 泛型参数在方法调用时,指明其具体类型
- 泛型方法可以根据需要声明为 static 的
- 泛型方法所属的类是否是一个泛型类都可以
面试 区分 Collection 和 Collections
Collection,集合框架中用于存储的一个一个元素接口,又分为 List 和 Set 等子接口
Collections,用于操作集合框架的一个工具类,此时的集合框架包括 Set List Map
Collections 工具类常用方法
排序:
- java
Collections.sort(list);
对列表进行升序排序。
洗牌:
- java
Collections.shuffle(list);
随机打乱列表中的元素顺序。
反转:
- java
Collections.reverse(list);
反转列表中元素的顺序。
查找最大值和最小值:
- java
Collections.max(collection);
Collections.min(collection);
返回集合中的最大值和最小值。
填充:
- java
Collections.fill(list, obj);
用指定的对象替换列表中的所有元素。
复制:
- java
Collections.copy(dest, src);
将源列表中的所有元素复制到目标列表中。
不可变集合:
- java
List<String> immutableList = Collections.unmodifiableList(list);
返回一个不可修改的列表。
import java.util.*;
public class CollectionsTest {
/*
* reverse(list) 反转List中的元素排序
* shuffle(List)集合元素进行随机排序
* sort(List)根据元素的自然排序对指定List集合元素按升序排序
* sort(List,Comparator)根据指定的Comparator产生的顺序对List集合进行排序
* swap(List,int,int)将指定List集合的i处元素和j处元素进行交换
* */
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(45, 43, 65, 6);
System.out.println(list);
//[45, 43, 65, 6]
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
//[6, 65, 43, 45]
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1; // 降序排序
}
});
System.out.println(list);
//[65, 45, 43, 6]
int count = Collections.frequency(list, 45);
System.out.println("45出现了"+count+"次");
//45出现了1次
}
}
class Test{
//复制
public static void main(String[] args) {
List src = Arrays.asList(45, 43, 65, 6);
List dest = Arrays.asList(new Object[src.size()]);
Collections.copy(dest, src);
System.out.println(dest);
//[45, 43, 65, 6]
}
}
class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//提供了多个unmodfiableXxx()方法,该方法返回指定的Xxx的不可修改视图
List list1 = new ArrayList();
//list1可以写入数据
list1.add(34);
list1.add(12);
List List2 = Collections.unmodifiableList(list1);
System.out.println(List2);
//list2只能读不能写
List2.add(34);
System.out.println(List2);
/*Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
at java.base/java.util.Collections$UnmodifiableCollection.add(Collections.java:1092)
at Test2.main(CollectionsTest.java:54)*/
}
}
class Test3{
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list1 = new ArrayList();
List list2 = Collections.unmodifiableList(list1);
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
Map map2 = Collections.synchronizedMap(map1);
//返回的map2是线程安全的
}
}
7. Collections工具类
参考操作数组的工具类:Arrays,Collections 是一个操作 Set、List 和 Map 等集合的工具类。
7.1 常用方法
Collections 中提供了一系列静态的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改等操作,还提供了对集合对象设置不可变、对集合对象实现同步控制等方法(均为static方法):
排序操作:
- reverse(List):反转 List 中元素的顺序
- shuffle(List):对 List 集合元素进行随机排序
- sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
- sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
- swap(List,int, int):将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
查找
- Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object max(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object min(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素
- Object min(Collection,Comparator):根据 Comparator 指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素
- int binarySearch(List list,T key)在List集合中查找某个元素的下标,但是List的元素必须是T或T的子类对象,而且必须是可比较大小的,即支持自然排序的。而且集合也事先必须是有序的,否则结果不确定。
- int binarySearch(List list,T key,Comparator c)在List集合中查找某个元素的下标,但是List的元素必须是T或T的子类对象,而且集合也事先必须是按照c比较器规则进行排序过的,否则结果不确定。
- int frequency(Collection c,Object o):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
复制、替换
- void copy(List dest,List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中
- boolean replaceAll(List list,Object oldVal,Object newVal):使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值
- 提供了多个unmodifiableXxx()方法,该方法返回指定 Xxx的不可修改的视图。
添加
- boolean addAll(Collection c,T... elements)将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。
同步
- Collections 类中提供了多个 synchronizedXxx() 方法,该方法可使将指定集合包装成线程同步的集合,从而可以解决多线程并发访问集合时的线程安全问题:
7.2 举例
package com.atguigu.collections;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.Collator;
import java.util.*;
public class TestCollections {
@Test
public void test01(){
/*
public static <T> boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c,T... elements)
将所有指定元素添加到指定 collection 中。Collection的集合的元素类型必须>=T类型
*/
Collection<Object> coll = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coll, "hello","java");
Collections.addAll(coll, 1,2,3,4);
Collection<String> coll2 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coll2, "hello","java");
//Collections.addAll(coll2, 1,2,3,4);//String和Integer之间没有父子类关系
}
@Test
public void test02(){
/*
* public static <T extends Object & Comparable<? super T>> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll)
* 在coll集合中找出最大的元素,集合中的对象必须是T或T的子类对象,而且支持自然排序
*
* public static <T> T max(Collection<? extends T> coll,Comparator<? super T> comp)
* 在coll集合中找出最大的元素,集合中的对象必须是T或T的子类对象,按照比较器comp找出最大者
*
*/
List<Man> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Man("张三",23));
list.add(new Man("李四",24));
list.add(new Man("王五",25));
/*
* Man max = Collections.max(list);//要求Man实现Comparable接口,或者父类实现
* System.out.println(max);
*/
Man max = Collections.max(list, new Comparator<Man>() {
@Override
public int compare(Man o1, Man o2) {
return o2.getAge()-o2.getAge();
}
});
System.out.println(max);
}
@Test
public void test03(){
/*
* public static void reverse(List<?> list)
* 反转指定列表List中元素的顺序。
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");
System.out.println(list);
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test04(){
/*
* public static void shuffle(List<?> list)
* List 集合元素进行随机排序,类似洗牌,打乱顺序
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test05() {
/*
* public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List<T> list)
* 根据元素的自然顺序对指定 List 集合元素按升序排序
*
* public static <T> void sort(List<T> list,Comparator<? super T> c)
* 根据指定的 Comparator 产生的顺序对 List 集合元素进行排序
*/
List<Man> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Man("张三",23));
list.add(new Man("李四",24));
list.add(new Man("王五",25));
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Man>() {
@Override
public int compare(Man o1, Man o2) {
return Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA).compare(o1.getName(),o2.getName());
}
});
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test06(){
/*
* public static void swap(List<?> list,int i,int j)
* 将指定 list 集合中的 i 处元素和 j 处元素进行交换
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world");
Collections.swap(list,0,2);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test07(){
/*
* public static int frequency(Collection<?> c,Object o)
* 返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world","hello","hello");
int count = Collections.frequency(list, "hello");
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
@Test
public void test08(){
/*
* public static <T> void copy(List<? super T> dest,List<? extends T> src)
* 将src中的内容复制到dest中
*/
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){//1-5
list.add(i);
}
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=11; i<=13; i++){//11-13
list2.add(i);
}
Collections.copy(list, list2);
System.out.println(list);
List<Integer> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=11; i<=20; i++){//11-20
list3.add(i);
}
//java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Source does not fit in dest
//Collections.copy(list, list3);
//System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test09(){
/*
* public static <T> boolean replaceAll(List<T> list,T oldVal,T newVal)
* 使用新值替换 List 对象的所有旧值
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"hello","java","world","hello","hello");
Collections.replaceAll(list, "hello","song");
System.out.println(list);
}
}7.3 练习
练习1:
请从键盘随机输入10个整数保存到List中,并按倒序、从大到小的顺序显示出来
**练习2:**模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌,牌没有排序
效果演示:
提示:
String[] num = {"A","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K"};
String[] color = {"方片","梅花","红桃","黑桃"};
ArrayList<String> poker = new ArrayList<>();代码示例:
/**
*
* @author 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @date 2022年5月7日上午12:26:59
*
*/
public class PokerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] num = {"A","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K"};
String[] color = {"方片","梅花","红桃","黑桃"};
ArrayList poker = new ArrayList();
//1. 生成54张扑克牌
for (String s1 : color) {
for (String s2 : num) {
poker.add(s1.concat(" " + s2));
}
}
poker.add("小王");
poker.add("大王");
//2. 洗牌
Collections.shuffle(poker);
//3. 发牌
ArrayList tomCards = new ArrayList();
ArrayList jerryCards = new ArrayList();
ArrayList meCards = new ArrayList();
ArrayList lastCards = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < poker.size(); i++) {
if(i >= poker.size() - 3){
lastCards.add(poker.get(i));
}else if(i % 3 == 0){
tomCards.add(poker.get(i));
}else if(i % 3 == 1){
jerryCards.add(poker.get(i));
}else {
meCards.add(poker.get(i));
}
}
//4. 看牌
System.out.println("Tom:\n" + tomCards);
System.out.println("Jerry:\n" + jerryCards);
System.out.println("me:\n" + meCards);
System.out.println("底牌:\n" + lastCards);
}
}**练习3:**模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌并对牌进行排序的代码实现。
提示:考查HashMap、TreeSet、ArrayList、Collections
代码示例:
/**
* @author 尚硅谷-宋红康
* @create 0:23
*/
public class PokerTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] num = {"3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "J", "Q", "K", "A", "2"};
String[] color = {"方片", "梅花", "红桃", "黑桃"};
HashMap map = new HashMap(); // 存储索引和扑克牌
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); // 存储索引
int index = 0; // 索引的开始值
for (String s1 : num) {
for (String s2 : color) {
map.put(index, s2.concat(s1)); // 将索引和扑克牌添加到HashMap中
list.add(index); // 将索引添加到ArrayList集合中
index++;
}
}
map.put(index, "小王");
list.add(index);
index++;
map.put(index, "大王");
list.add(index);
// 洗牌
Collections.shuffle(list);
// 发牌
TreeSet Tom = new TreeSet();
TreeSet Jerry = new TreeSet();
TreeSet me = new TreeSet();
TreeSet lastCards = new TreeSet();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (i >= list.size() - 3) {
lastCards.add(list.get(i)); // 将list集合中的索引添加到TreeSet集合中会自动排序
} else if (i % 3 == 0) {
Tom.add(list.get(i));
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
Jerry.add(list.get(i));
} else {
me.add(list.get(i));
}
}
// 看牌
lookPoker("Tom", Tom, map);
lookPoker("Jerry", Jerry, map);
lookPoker("康师傅", me, map);
lookPoker("底牌", lastCards, map);
}
public static void lookPoker(String name, TreeSet ts, HashMap map) {
System.out.println(name + "的牌是:");
for (Object index : ts) {
System.out.print(map.get(index) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}